A head injury from car accident can be a severe experience that requires immediate and informed action. Understanding the symptoms, knowing the steps to take immediately after the incident, and recognizing the importance of recovery can significantly affect long-term outcomes. This article will guide you through each of these aspects.
Understanding the Severity of a Head Injury
Head injuries can vary dramatically in severity, and distinguishing between them is crucial to determining the appropriate course of action. Understanding these differences can help you seek the necessary medical treatment promptly and effectively.
Identifying Mild, Moderate, and Severe Head Injuries
Mild Head Injuries (Concussions): These may cause temporary confusion, dizziness, or headaches and often resolve with rest. However, lingering symptoms such as fatigue and difficulty concentrating—referred to as post-concussion syndrome—can persist and significantly affect daily life.
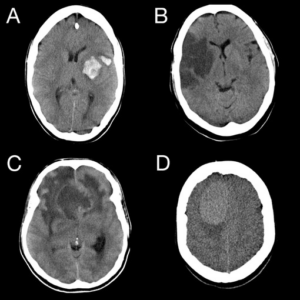
Moderate Head Injuries: Symptoms include persistent headaches, nausea, and difficulty concentrating. Medical evaluation, often including imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs, is essential to rule out complications such as internal bleeding or swelling.
Severe Head Injuries (Traumatic Brain Injuries or TBIs): These can result in loss of consciousness, seizures, or impaired coordination. Immediate medical attention is critical, as TBIs often lead to long-term cognitive, emotional, and physical impairments. Rehabilitation typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including physical therapy and neuropsychological support, to aid recovery.

Immediate Symptoms to Look Out For
Post-accident, it is crucial to monitor yourself and others for a range of symptoms that may indicate the severity of the head injury. Common symptoms include:
- Loss of consciousness
- Severe headache
- Confusion or disorientation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or balance issues
- Unusual behavior or personality changes
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
If any of these symptoms manifest, seeking prompt medical attention is imperative to assess and address the injury appropriately. Additionally, it is important to be aware that symptoms may not always appear immediately. Delayed symptoms can occur hours or even days after the initial injury, making it essential to remain vigilant and seek help if any concerning changes arise.
This awareness can be particularly important for parents and caregivers, who should closely monitor children after a head injury, as they may not always communicate their symptoms effectively.
What to Do After a Head Injury from a Car Accident
A head injury sustained during a car accident can be a serious and life-altering event. Immediate action, understanding symptoms, and following a structured recovery plan are vital for minimizing long-term impacts. This guide will help you navigate the critical steps to take after such an incident.
Understanding the Severity of a Head Injury
Head injuries can range from mild to severe, and identifying their severity is crucial for determining the appropriate course of action.
Mild, Moderate, and Severe Head Injuries
- Mild Head Injuries (Concussions): These may cause temporary confusion, dizziness, or headaches and often resolve with rest. However, lingering symptoms such as fatigue and difficulty concentrating—referred to as post-concussion syndrome—can persist and significantly affect daily life.
- Moderate Head Injuries: Symptoms include persistent headaches, nausea, and difficulty concentrating. Medical evaluation, often including imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs, is essential to rule out complications such as internal bleeding or swelling.
- Severe Head Injuries (Traumatic Brain Injuries or TBIs): These can result in loss of consciousness, seizures, or impaired coordination. Immediate medical attention is critical, as TBIs often lead to long-term cognitive, emotional, and physical impairments. Rehabilitation typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including physical therapy and neuropsychological support, to aid recovery.
For additional guidance on recognizing and managing TBIs, visit CDC Traumatic Brain Injury Basics.
Immediate Symptoms to Monitor
After an accident, watch for symptoms that may indicate a head injury:
- Loss of consciousness
- Severe headache
- Confusion or disorientation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or balance issues
- Personality changes or difficulty speaking
These symptoms can manifest hours or even days later, emphasizing the need for vigilance and prompt medical attention.
Immediate Steps to Take Post-Accident
Seek Medical Attention
Even if symptoms appear mild, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Imaging tests like MRIs or CT scans can help identify hidden injuries. Following medical advice for rest and follow-up care is essential for detecting delayed symptoms, such as persistent headaches or confusion.
Report the Incident
Document the accident by reporting it to authorities and collecting information, such as the other party’s contact and insurance details. Photos of the scene, vehicle damage, and visible injuries can serve as critical evidence for insurance claims or legal actions.
If you are navigating the legal complexities of a car accident, consult professionals like Howe Law to ensure your rights are protected and you receive the care and compensation you deserve.
The Importance of Post-Injury Rest
Rest after a head injury is critical to promote healing and allow the brain to recover. It helps alleviate symptoms and prevents further aggravation of the condition.
The Role of Rest in Recovery
Research indicates that adequate rest leads to better recovery rates following a head injury. Rest allows the brain to repair, reducing the risk of complications or prolonged symptoms.
This period of rest should not only focus on physical inactivity but also on limiting cognitive activities such as screen time, reading, and intense conversations. Creating a calm environment can facilitate healing.
Moreover, the brain is an incredibly complex organ that requires time to reorganize and heal after trauma. During this recovery phase, neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to adapt and form new connections—plays a crucial role. Adequate rest can enhance this natural process, allowing for improved cognitive function and emotional stability as the brain recuperates from injury.
Tips for Effective Rest and Recuperation
To optimize your recovery, consider the following tips:
- Establish a quiet, comfortable space free from bright lights and loud noises.
- Limit screen time, including mobile devices and computers, to avoid triggering symptoms.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet to support overall health.
- Gradually reintroduce activities according to your healthcare provider’s advice.
- Engage in light physical activities only if recommended and under supervision.
Following these guidelines can improve recovery and reduce complications after a head injury. Mindfulness practices like meditation or gentle yoga promote relaxation and reduce anxiety, supporting mental and physical healing. Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for monitoring progress and tailoring your recovery plan. Each healing journey is unique, so listening to your body and adapting as needed is key to achieving full recovery.
Long-Term Effects of a Head Injury
Head injuries can have enduring consequences impacting both physical health and psychological well-being. Awareness of these potential long-term effects can help individuals and families prepare for what may lie ahead.
Physical Consequences of a Head Injury
Depending on the severity of the injury, individuals may experience ongoing physical issues, such as headaches, balance difficulties, or chronic pain. These symptoms can affect daily activities and overall quality of life.
Some individuals may also face increased sensitivity to light and sound, which can complicate social interactions and general functioning. Rehabilitation and targeted therapy can aid in addressing these lingering physical challenges. Additionally, some may experience cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with memory, attention, and processing speed, which can further hinder their ability to engage in work or educational settings. Occupational therapy can be particularly beneficial in helping individuals regain lost skills and adapt to their new circumstances.
Psychological Impact of a Head Injury
The psychological effects of head injuries can be as significant as physical consequences. Many individuals report experiences of anxiety, depression, or changes in mood following an accident.
These psychological challenges can impact relationships, job performance, and overall mental well-being. Seeking support from mental health professionals as part of comprehensive rehabilitation is essential for individuals struggling with these issues. Furthermore, the unpredictability of mood swings and emotional responses can strain family dynamics, making it crucial for loved ones to also receive education and support. Understanding the nature of these psychological impacts can foster empathy and patience, allowing families to navigate the complexities of recovery together.
Rehabilitation and Therapy Options
A comprehensive treatment plan after a head injury frequently incorporates rehabilitation and therapy options tailored to individual needs. These practices can provide significant support to foster recovery.
Physical Therapy for Head Injury Recovery
Physical therapy can be essential in regaining strength, balance, and coordination following a head injury. A trained therapist can develop a personalized program to restore physical capabilities while addressing any specific deficits.
Regular sessions may include exercises designed to improve gross motor skills, flexibility, and overall physical fitness, all of which are critical for a successful recovery. Additionally, therapists often incorporate techniques such as proprioceptive training, which enhances the body’s ability to sense its position in space, thereby improving balance and reducing the risk of falls. This is particularly important for individuals who may experience dizziness or instability as a result of their injury.

Cognitive Therapy for Mental Health Support
Cognitive therapy plays a vital role in addressing the psychological repercussions of a head injury. Targeted therapy can help individuals cope with anxiety, depression, and memory issues.
Professional support fosters mental resilience, assists patients in developing effective coping mechanisms, and helps navigate social reintegration following a head injury.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), for instance, can be particularly beneficial as it encourages individuals to identify and challenge negative thought patterns that may arise post-injury. Furthermore, group therapy sessions can provide a sense of community and shared experience, allowing individuals to connect with others who are facing similar challenges, thereby reducing feelings of isolation and promoting emotional healing.
Conclusion
A head injury from a car accident requires immediate attention, ongoing vigilance, and a structured recovery plan. Seeking prompt medical evaluation, documenting the incident, and prioritizing rest are crucial steps to ensure a smooth recovery. For legal guidance and support following an accident, Howe Law can assist in securing compensation and accessing essential resources.
Recovery is a journey, but with the right actions and support, individuals can reclaim their quality of life and move forward confidently.
Related Articles